⚠️ Sunset Notice: This service will be discontinued as of September 30th, 2023. Learn more »
Did you come here for Live Video Shopping?
This is documentation for Bambuser Live Streaming SDK.
If you're looking for documentation regarding Live Video Shopping (opens new window) , see these pages (opens new window)
How to create a live video player app in Swift using XCode
This guide is based on Xcode 12.2.
This guide focuses on the bare minimum required to play broadcasts. Make sure to familiarize yourself with the example apps in the SDK bundles for a more complete overview.
Choose your environment:
Xcode and Swift
Open Xcode.
Select
File -> New -> Project...Choose the
Apptemplate.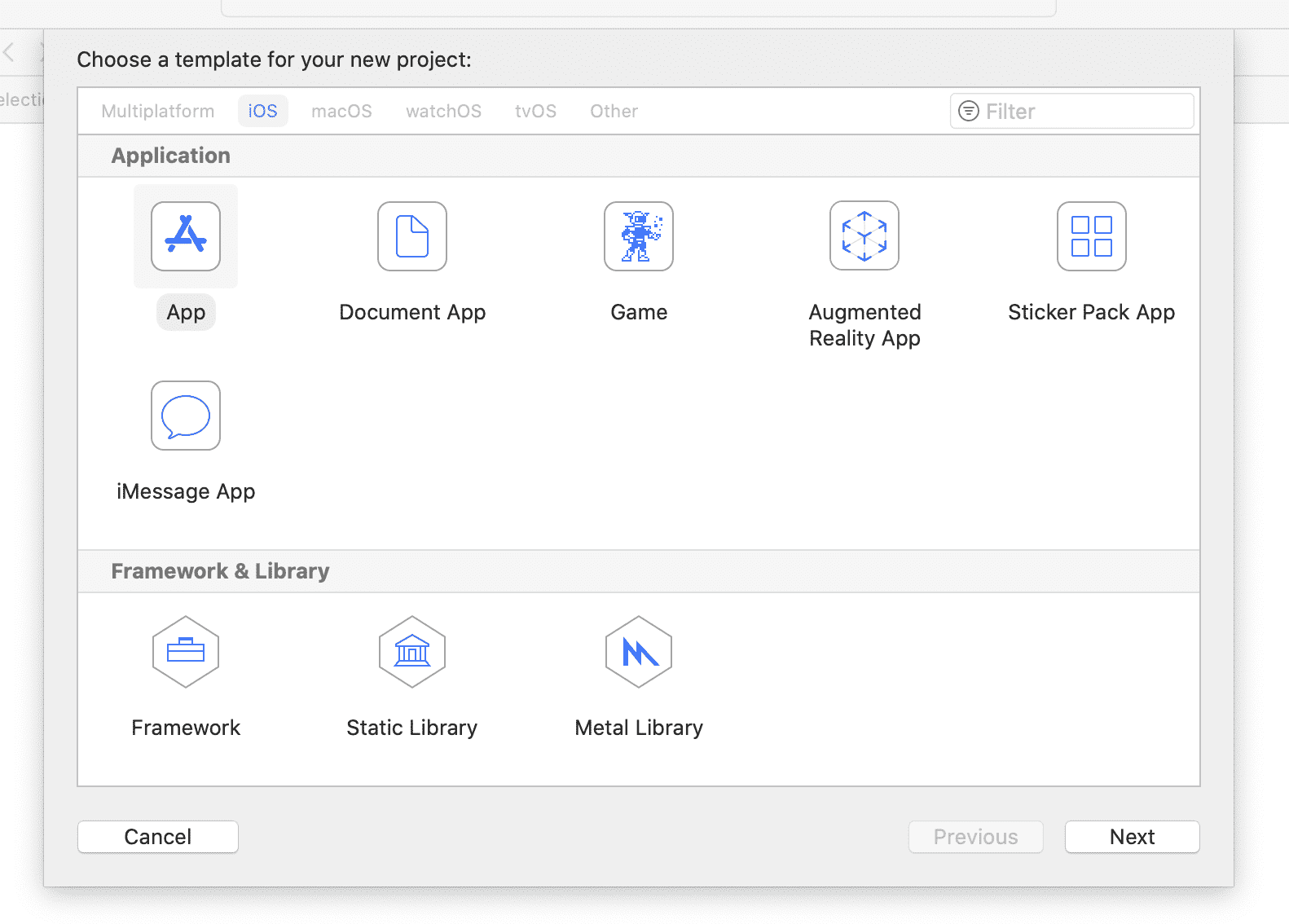
Enter a suitable product name and add your team and your organization identifier
Ensure
Swiftis the selected language. Or see the Objective-C guide if you prefer Objective-C.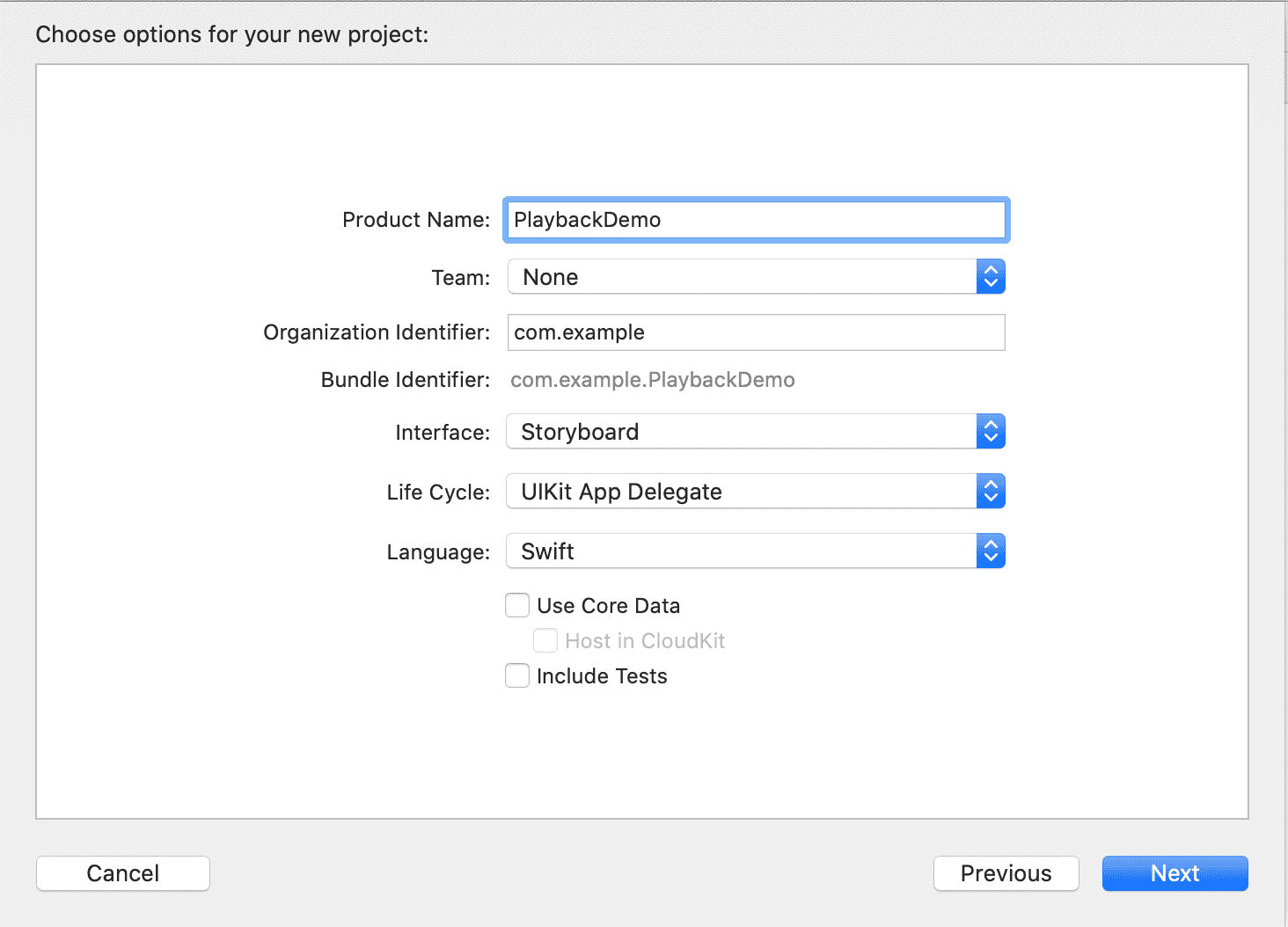
Add dependencies
Installing dependencies using Swift Package Manager
You can use Swift Package Manager to install the Bambuser SDK:s.
Add
https://github.com/bambuser/bambuser-sdk-iosto your Xcode project orPackage.swiftfile.Select the
1.0.4version to get the latest SDK:s.Xcode will then update the SDK:s automatically, depending on the version rule you choose.
Installing dependencies using CocoaPods
If your development environment is set up for it, you can use CocoaPods (opens new window) to install the Bambuser SDK:s.
Prepare the newly created project for CocoaPods use with
pod init.Add
pod 'libbambuser-ios', '1.0.4'to your Podfile.Run
pod installto fetch the SDK and configure the project.
Installing dependencies manually
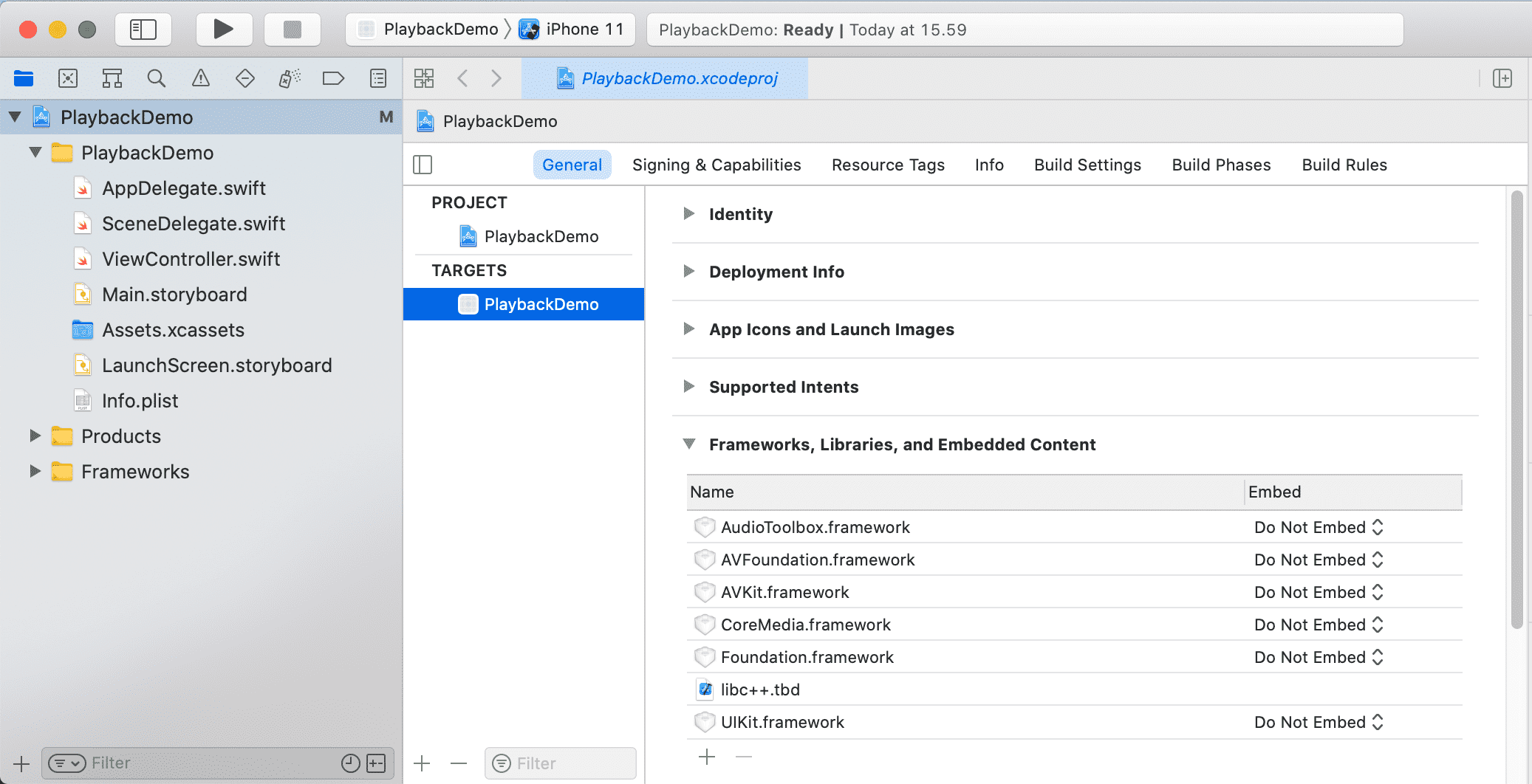
The Bambuser playback library has the following dependencies:
AudioToolbox,AVFoundation,AVKit,CoreMedia,Foundation,libc++.tbdandUIKit.
Add the playback SDK
Log in to the Bambuser site and download the latest iOS SDK bundle from the Developer (opens new window) page.
Open up Finder and navigate to the download folder, then double click the SDK bundle to unzip it.
Go to the
Frameworksdirectory in the SDK bundle and dragBambuserPlayer.xcframeworkinto theFrameworkssection of your Xcode project's file tree navigator.
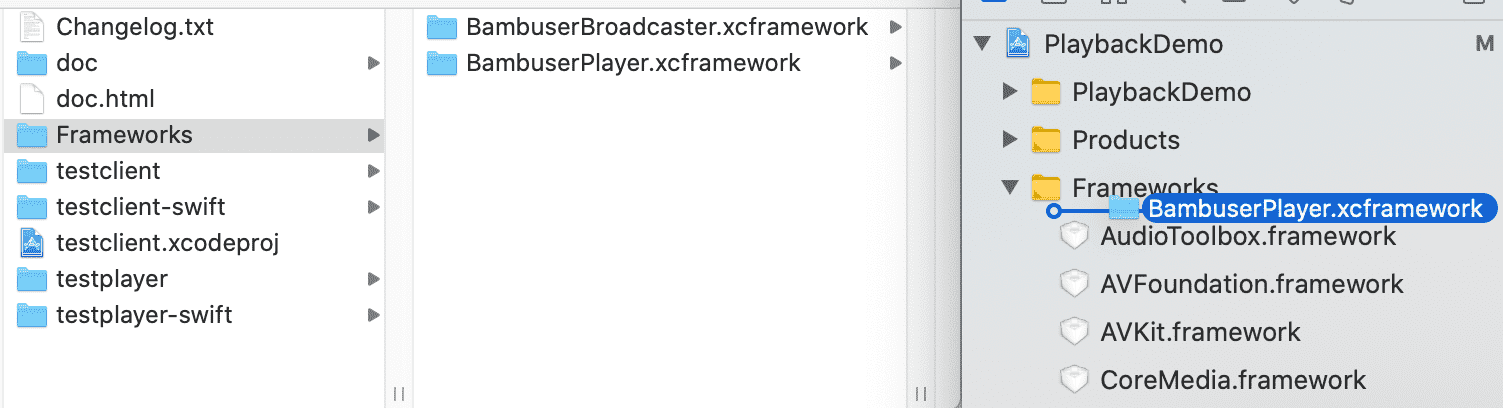
- Check
Copy items if neededto ensure that your project folder gets its own copy of the files.
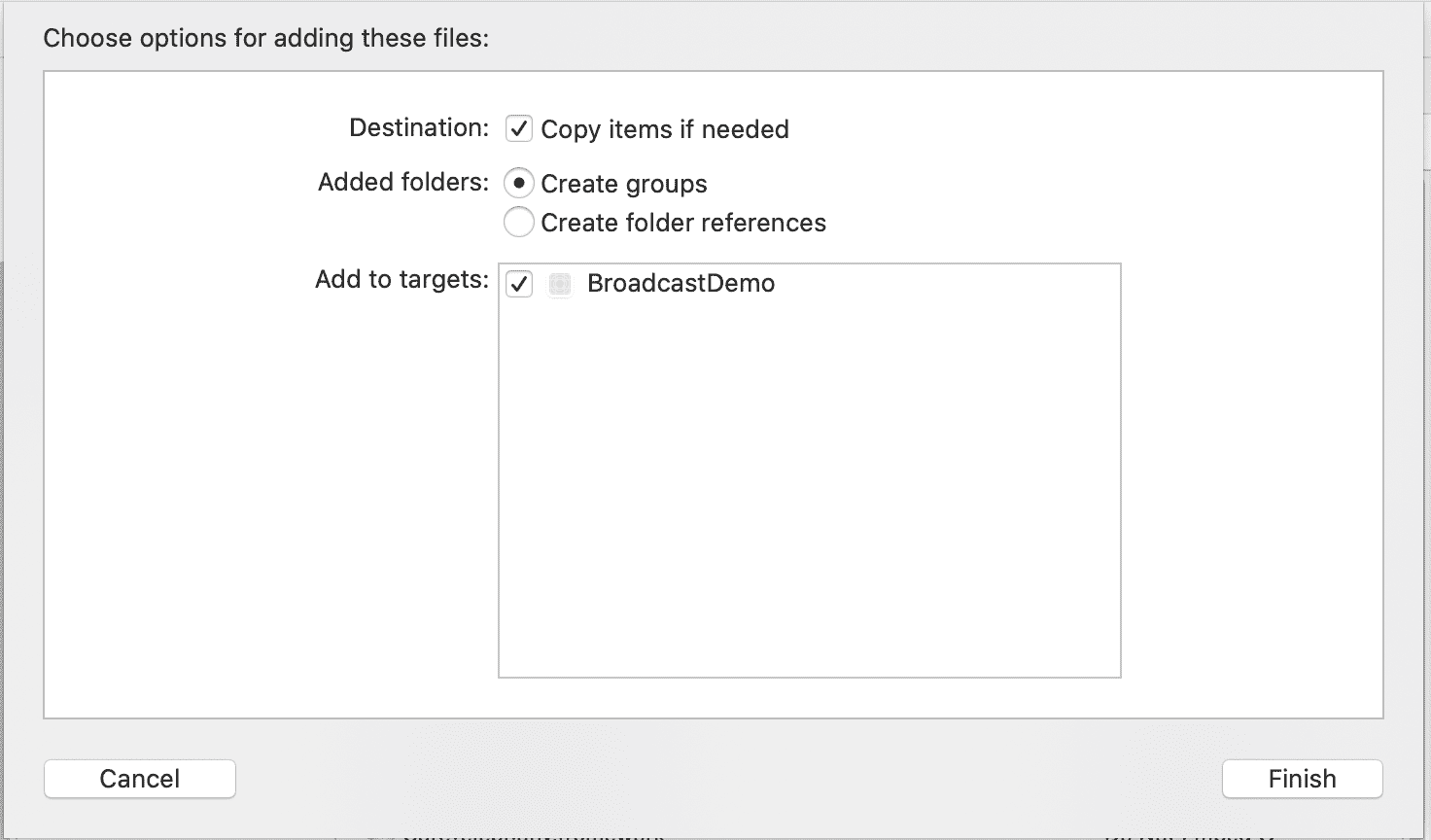
- The act of adding
BambuserPlayer.xcframeworkintoFrameworksshould also have addedBambuserPlayer.xcframeworktoFrameworks, Libraries and Embedded ContentunderGeneral.
Add a BambuserPlayer
Now that you have installed the dependencies it's time to start using the SDK.
In ViewController.swift import BambuserPlayer and add a BambuserPlayer (opens new window) variable to your ViewController.
import BambuserPlayer
var bambuserPlayer: BambuserPlayer
Add the player view
In ViewController.swift in the viewDidLoad method, add the player view
to the view hierarchy.
self.view.addSubview(bambuserPlayer)
In ViewController.swift add a viewWillLayoutSubviews method, then add some code
to ensure the player view is assigned the desired dimensions.
override func viewWillLayoutSubviews() {
let statusBarOffset = self.topLayoutGuide.length
bambuserPlayer.frame = CGRect(x: 0, y: 0 + statusBarOffset, width: self.view.bounds.size.width, height: self.view.bounds.size.height - statusBarOffset)
}
Authentication
To be allowed to retrieve broadcasts, your app needs to identify itself to Bambuser.
Head over to the Developer (opens new window) page on the
Bambuser site again and get the Sandbox application ID,
then assign it to BambuserPlayer (opens new window) in ViewController.swift directly after initialization.
Remember to replace the Sandbox id with a Production application ID before you release your app!
bambuserPlayer.applicationId = "GFZalqkR5iyZcIgaolQmA"
We will also need a signed resource URI for the broadcast we want to play. For the scope of this guide, we will use a pre-signed resource URI supplied in the example application distributed with the Bambuser iOS SDK bundle. To learn how to sign your own resource URIs, refer to the chapter on Resource URI.
bambuserPlayer.playVideo("https://cdn.bambuser.net/broadcasts/ec968ec1-2fd9-f8f3-4f0a-d8e19dccd739?da_signature_method=HMAC-SHA256&da_id=432cebc3-4fde-5cbb-e82f-88b013140ebe&da_timestamp=1456740399&da_static=1&da_ttl=0&da_signature=8e0f9b98397c53e58f9d06d362e1de3cb6b69494e5d0e441307dfc9f854a2479")
Add playback controls
Let's add some buttons to be able to control the playback.
In ViewController.swift, declare the following buttons:
class ViewController: UIViewController {
var bambuserPlayer: BambuserPlayer
var playButton: UIButton
var pauseButton: UIButton
var rewindButton: UIButton
...
In ViewController.swift, in the viewDidLoad method, initialize the buttons
and add them to the view hierarchy:
playButton.setTitle("Play", for: UIControl.State.normal)
playButton.addTarget(bambuserPlayer, action: #selector(BambuserPlayer.playVideo as (BambuserPlayer) -> () -> Void), for: UIControl.Event.touchUpInside)
self.view.addSubview(playButton)
pauseButton.setTitle("Pause", for: UIControl.State.normal)
pauseButton.addTarget(bambuserPlayer, action: #selector(BambuserPlayer.pauseVideo as (BambuserPlayer) -> () -> Void), for: UIControl.Event.touchUpInside)
self.view.addSubview(pauseButton)
rewindButton.setTitle("Rewind", for: UIControl.State.normal)
rewindButton.addTarget(self, action: #selector(ViewController.rewind), for: UIControl.Event.touchUpInside)
self.view.addSubview(rewindButton)
In ViewController.swift, in the viewWillLayoutSubviews method, position
the buttons to taste
playButton.frame = CGRect(x: 20, y: 20 + statusBarOffset, width: 100, height: 40)
pauseButton.frame = CGRect(x: 20, y: 80 + statusBarOffset, width: 100, height: 40)
rewindButton.frame = CGRect(x: 20, y: 140 + statusBarOffset, width: 100, height: 40)
Also add a new method to handle the rewind action
@objc func rewind() {
bambuserPlayer.seek(to: 0.0);
}
Subscribe to events
To know what's going on inside BambuserPlayer (opens new window), we should hook up ourself as
its delegate. In ViewController.swift, assign self to bambuserPlayer.delegate
directly after initialization:
bambuserPlayer.delegate = self;
In ViewController.swift, we now need to declare that we support the
BambuserPlayerDelegate (opens new window) protocol:
class ViewController: UIViewController, BambuserPlayerDelegate {
Finally, we add a status callback method in ViewController.swift:
func playbackStatusChanged(_ status: BambuserPlayerState) {
switch status {
case kBambuserPlayerStatePlaying:
playButton.isEnabled = false
pauseButton.isEnabled = true
break
case kBambuserPlayerStatePaused:
playButton.isEnabled = true
pauseButton.isEnabled = false
break
case kBambuserPlayerStateStopped:
playButton.isEnabled = true
pauseButton.isEnabled = false
break
case kBambuserPlayerStateError:
NSLog("Failed to load video for %@", bambuserPlayer.resourceUri);
break
default:
break
}
}
Configuring AVAudioSession
Use AVAudioSession to configure the behavior of audio in the app. There are several possible categories you can choose from, but the AVAudioSessionCategoryPlayback (opens new window) is the most commonly used in a playback application. When using this category, audio continues with the Silent switch set to silent. If it is desired to honour the Silent switch then AVAudioSessionCategorySoloAmbient (opens new window)(deafult category) or AVAudioSessionCategoryAmbient (opens new window) are suitable options.
Read more about AVAudioSession in Apples documentation (opens new window).
do {
try AVAudioSession.sharedInstance().setCategory(.playback)
try AVAudioSession.sharedInstance().setActive(true)
} catch {
}
Putting it all together
The above steps should lead to a main view source somewhat along these lines:
ViewController.swift
import UIKit
import BambuserPlayer
class ViewController: UIViewController, BambuserPlayerDelegate {
var bambuserPlayer: BambuserPlayer
var playButton: UIButton
var pauseButton: UIButton
var rewindButton: UIButton
required init?(coder aDecoder: NSCoder) {
bambuserPlayer = BambuserPlayer()
playButton = UIButton(type: UIButton.ButtonType.system)
pauseButton = UIButton(type: UIButton.ButtonType.system)
rewindButton = UIButton(type: UIButton.ButtonType.system)
super.init(coder: aDecoder)
}
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
// Do any additional setup after loading the view, typically from a nib.
do {
try AVAudioSession.sharedInstance().setCategory(.playback)
try AVAudioSession.sharedInstance().setActive(true)
} catch {
}
bambuserPlayer.delegate = self
bambuserPlayer.applicationId = "GFZalqkR5iyZcIgaolQmA"
bambuserPlayer.playVideo("https://cdn.bambuser.net/broadcasts/ec968ec1-2fd9-f8f3-4f0a-d8e19dccd739?da_signature_method=HMAC-SHA256&da_id=432cebc3-4fde-5cbb-e82f-88b013140ebe&da_timestamp=1456740399&da_static=1&da_ttl=0&da_signature=8e0f9b98397c53e58f9d06d362e1de3cb6b69494e5d0e441307dfc9f854a2479")
self.view.addSubview(bambuserPlayer)
playButton.setTitle("Play", for: UIControl.State.normal)
playButton.addTarget(bambuserPlayer, action: #selector(BambuserPlayer.playVideo as (BambuserPlayer) -> () -> Void), for: UIControl.Event.touchUpInside)
self.view.addSubview(playButton)
pauseButton.setTitle("Pause", for: UIControl.State.normal)
pauseButton.addTarget(bambuserPlayer, action: #selector(BambuserPlayer.pauseVideo as (BambuserPlayer) -> () -> Void), for: UIControl.Event.touchUpInside)
self.view.addSubview(pauseButton)
rewindButton.setTitle("Rewind", for: UIControl.State.normal)
rewindButton.addTarget(self, action: #selector(ViewController.rewind), for: UIControl.Event.touchUpInside)
self.view.addSubview(rewindButton)
}
@objc func rewind() {
bambuserPlayer.seek(to: 0.0);
}
override func viewWillLayoutSubviews() {
let statusBarOffset = self.topLayoutGuide.length
bambuserPlayer.frame = CGRect(x: 0, y: 0 + statusBarOffset, width: self.view.bounds.size.width, height: self.view.bounds.size.height - statusBarOffset)
playButton.frame = CGRect(x: 20, y: 20 + statusBarOffset, width: 100, height: 40)
pauseButton.frame = CGRect(x: 20, y: 80 + statusBarOffset, width: 100, height: 40)
rewindButton.frame = CGRect(x: 20, y: 140 + statusBarOffset, width: 100, height: 40)
}
override func didReceiveMemoryWarning() {
super.didReceiveMemoryWarning()
// Dispose of any resources that can be recreated.
}
func playbackStatusChanged(_ status: BambuserPlayerState) {
switch status {
case kBambuserPlayerStatePlaying:
playButton.isEnabled = false
pauseButton.isEnabled = true
break
case kBambuserPlayerStatePaused:
playButton.isEnabled = true
pauseButton.isEnabled = false
break
case kBambuserPlayerStateStopped:
playButton.isEnabled = true
pauseButton.isEnabled = false
break
case kBambuserPlayerStateError:
NSLog("Failed to load video for %@", bambuserPlayer.resourceUri);
break
default:
break
}
}
}
Testing in the simulator
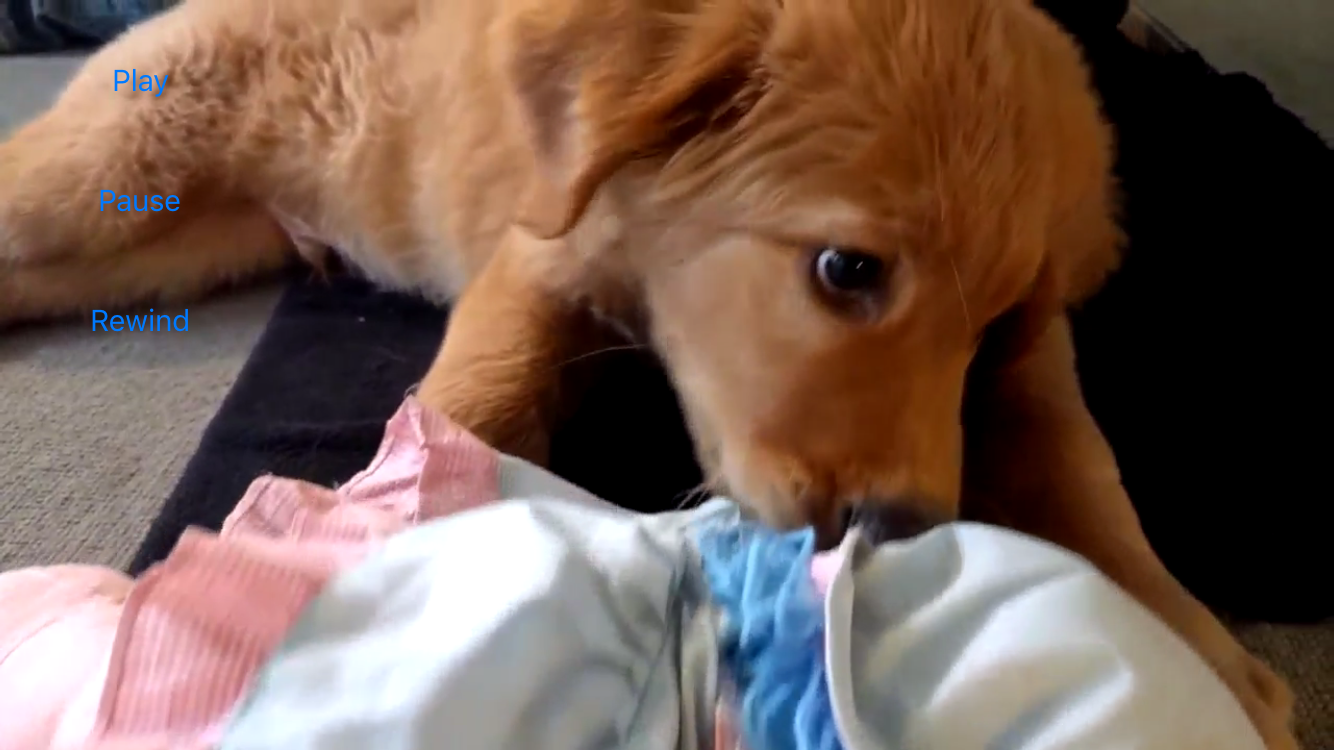
To test in the simulator, we just select a suitable simulator device as a target and click run.
If your applicationId and resourceUri were valid, you should see something like this.

Testing on a device
How to configure Xcode for ad-hoc development is out of scope for this guide.
Assuming you have all the required privileges, you should be able to tether
your iOS device to Xcode and click run.
If your applicationId and resourceUri were valid, you should see something like this.

